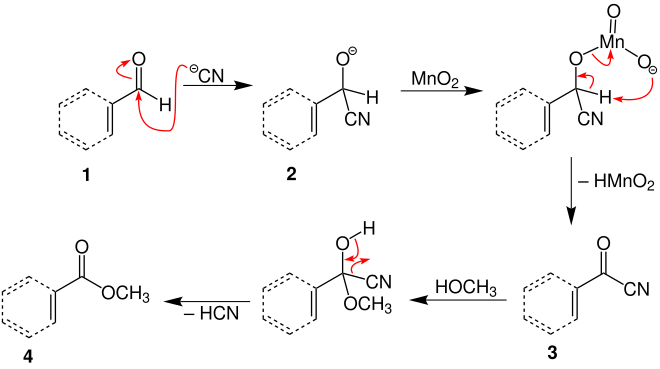
The Corey-Gilman ganem oxidation (also Corey-Ganem oxidation ), named after its discoverers EJ Corey , NW Gilman and BE Ganem, is a naming reaction from organic chemistry and was first published in 1968. The reaction describes the synthesis of esters from aldehydes or allylic alcohols .
An α,β-unsaturated aldehyde reacts to form an α,β-unsaturated methyl ester using manganese dioxide , potassium cyanide , and methanol .

Instead of the aldehyde, allyl alcohol can be used as starting material. Instead of methanol, another alcohol can be used for the esterification.
Example: Allyl alcohol reacts with the addition of manganese dioxide, potassium cyanide and ethanol to form ethyl acrylate :

The mechanism is described in the literature and is illustrated using the example of the overview reaction above: