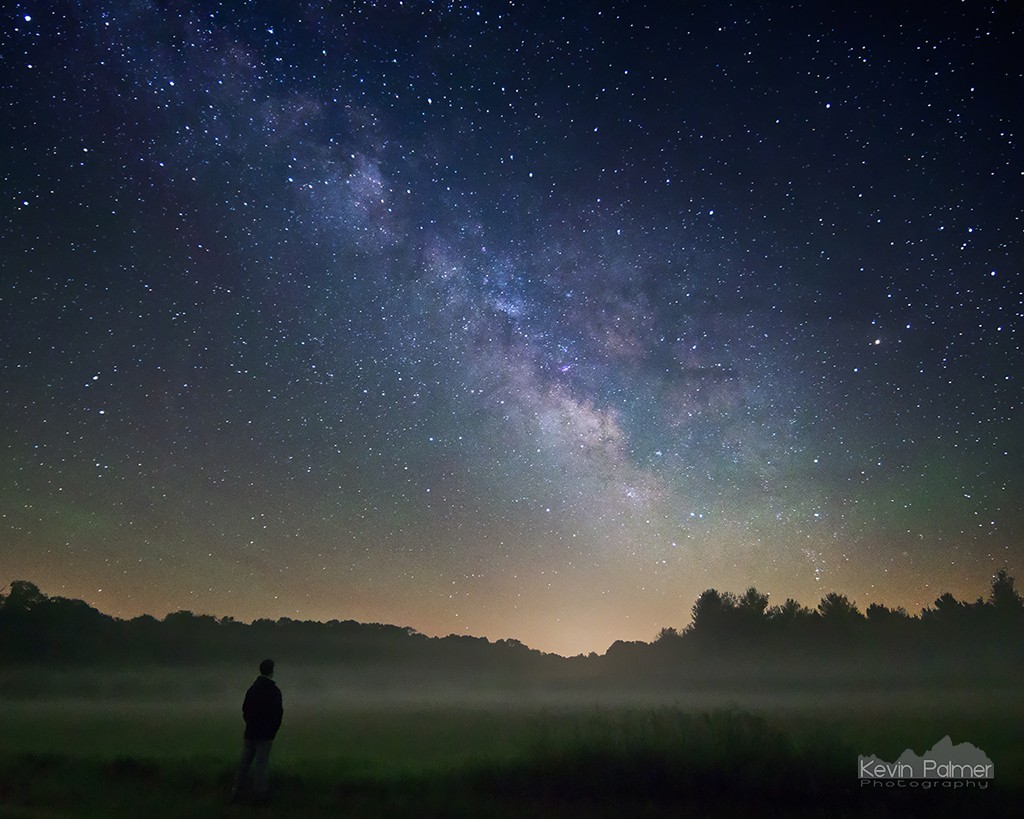
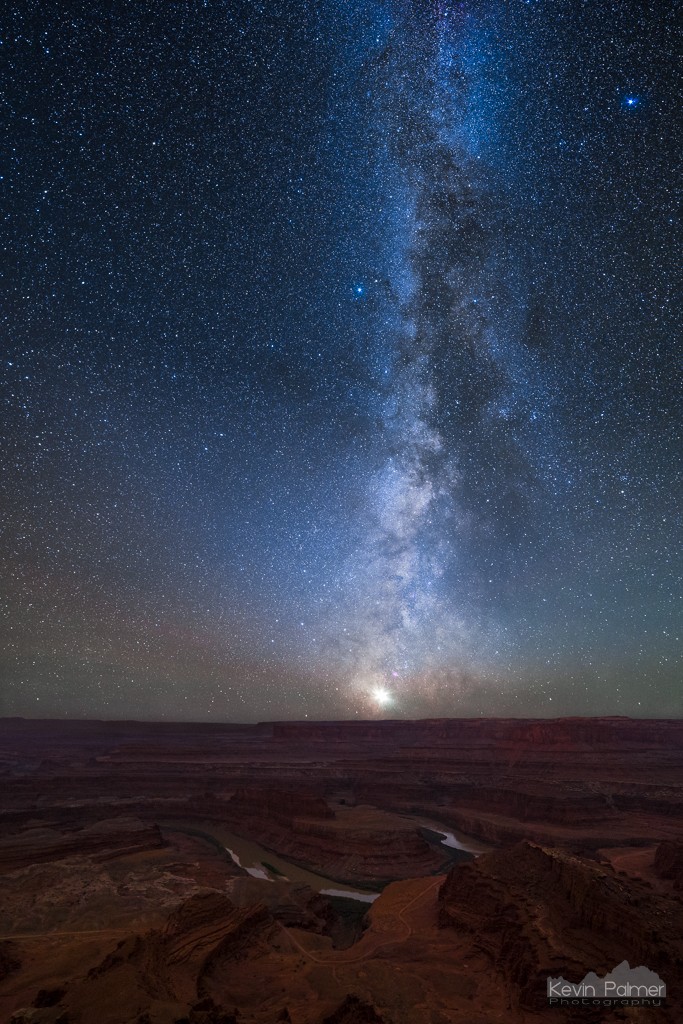
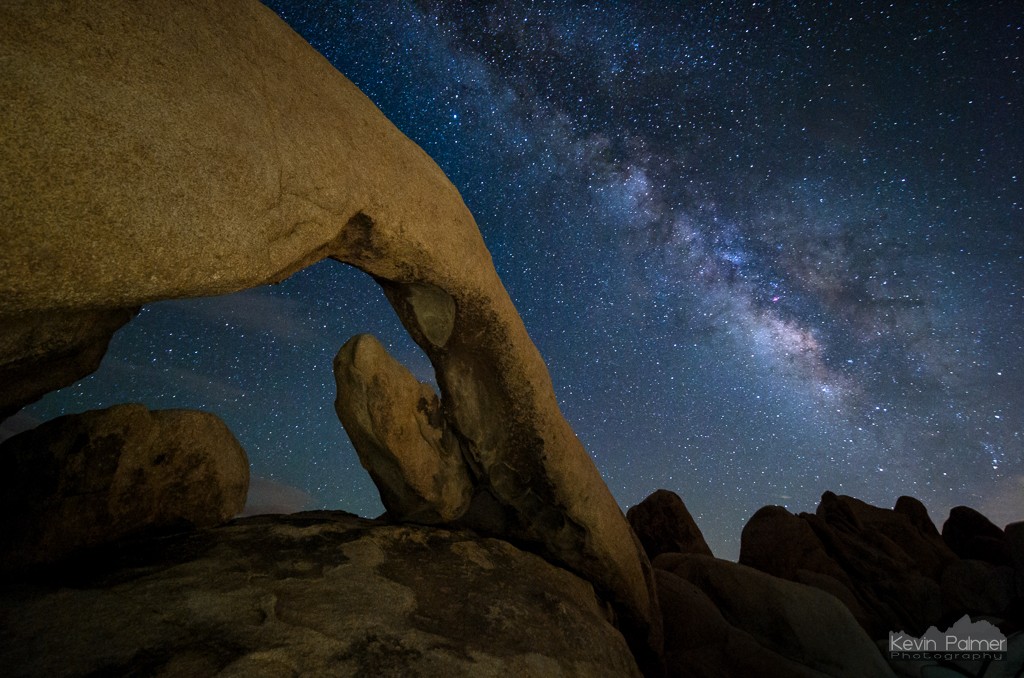
There are few views as awe-inspiring as seeing the milky way from a dark site. If someone unfamiliar with it sees a picture of the milky way without a terrestrial reference point, they might assume it was taken with a telescope. But the scale of the milky way is huge! You don’t need a telescope to see or photograph it. Binoculars or a telescope will certainly show you more detail, but they’re not a requirement. There have been many nights I’ve brought a telescope along for stargazing and haven’t even touched it.
A note about photos: A long exposure from a camera will pick up more stars and colors than the human eye can. The contrast on the photos can also be enhanced later, so the view doesn’t always match exactly what the naked eye sees. But what you can see with just your eyes under a truly dark sky is still spectacular.
A self portrait under the milky way
What is the Milky Way?
The milky way galaxy is one out of at least 100 billion in the universe. And the milky way itself contains about 100 billion stars. Our galaxy stretches 100,000 light years wide. Every star you can see with the unaided eye is located within the milky way. The only object you can see (without optical aid) in the sky outside of the milky way is the Andromeda Galaxy. Andromeda is over 2.5 million light years from earth; much too far to resolve individual stars without a powerful telescope.
But when most people talk about “seeing the milky way”, they are talking about the core of the galaxy. Located in the constellation Sagittarius, this is the brightest part of the milky way. Dust lanes, nebulas, and star clusters are all more concentrated in this area.
The purpose of DarkSiteFinder is to help you get away from light pollution and find a dark site to view the stars. But to see the milky way there are a few other factors you have to consider.
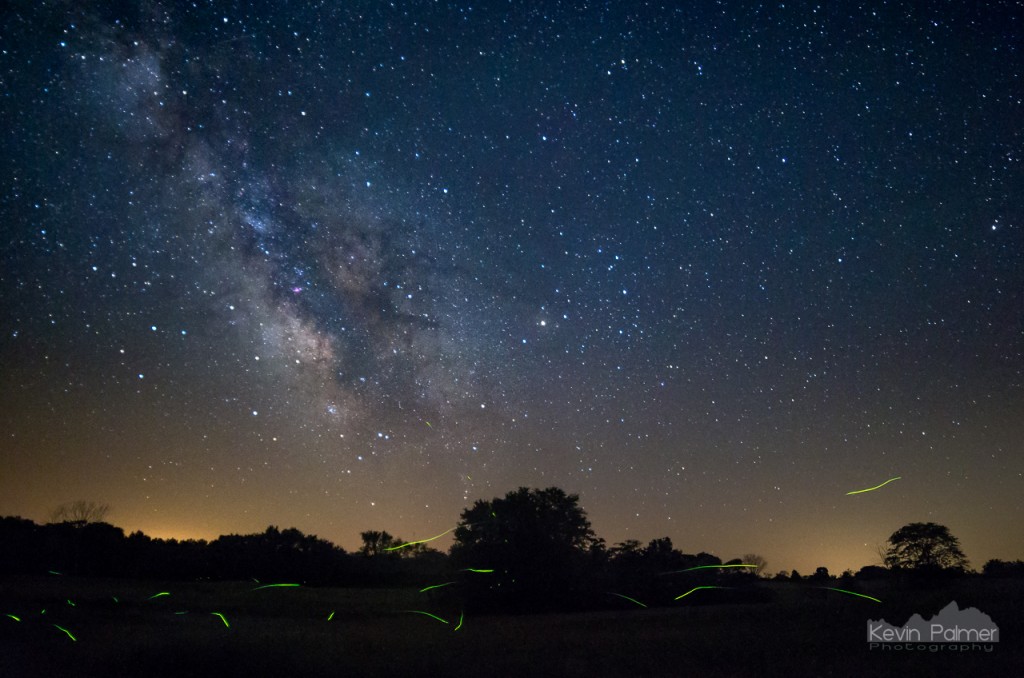
Midsummer nights are great, especially when fireflies join the show.
When is the Milky Way Visible?
The core of the milky way is only visible about half of the year. The other half it is located beneath the horizon. In the winter months (December – February) it is not visible at all because it’s too close to the sun. In the spring (March – May), it will first become visible a few hours before sunrise. By June it will rise much earlier before midnight. The summer months (June – August) are generally the best viewing time because it will be up most of the night. By fall (September – November) the milky way will be best seen in the evening, before it sets. Twilight can brighten the sky up to 2 hours before sunrise and 2 hours after sunset, so you want to avoid those times.
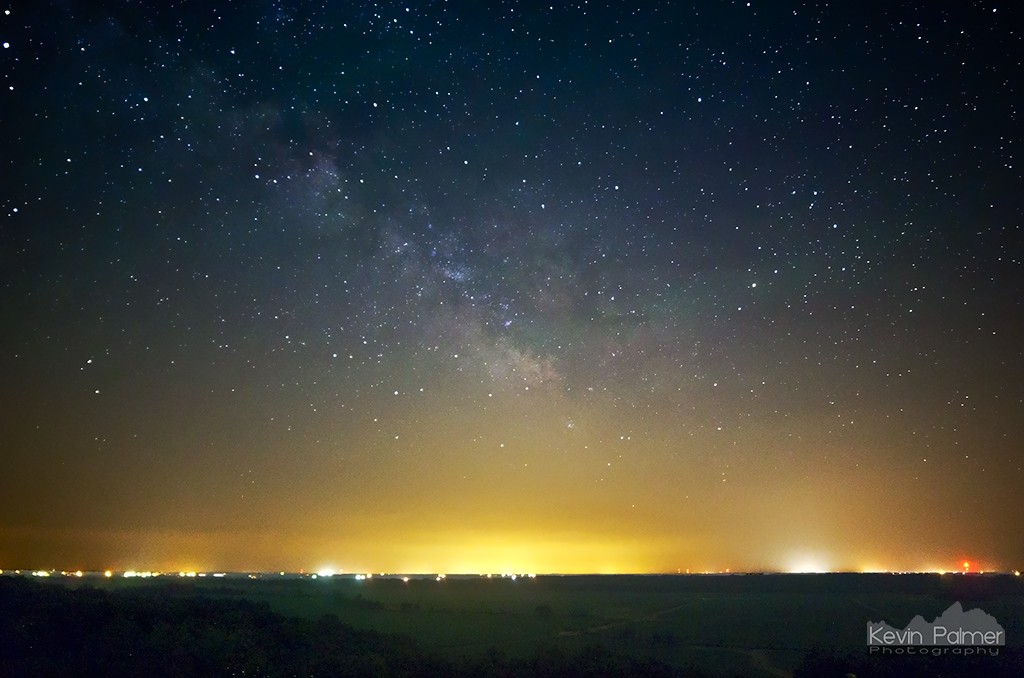
In Early November, the milky way was setting at the horizon by the time it got dark.
The rotation of the earth is what causes the stars to appear to move across the sky every night. But the earth does not actually take 24 hours to make a full rotation. It takes 23 hours and 56 minutes. This 4 minute difference is what causes the stars to change from night to night. Every night a given star will rise, cross the sky, or set 4 minutes earlier compared to the previous night. This change amounts to 2 hours every month. For example if the milky way rises at midnight tonight, a month from now it will be rising at 10pm. If you go out at the same time, the sky will look quite a bit different.
To get a better idea of the motion of the stars, download the free software Stellarium.
Watch the milky way rise in this time lapse video shot in the early morning hours at the end of April.
Location
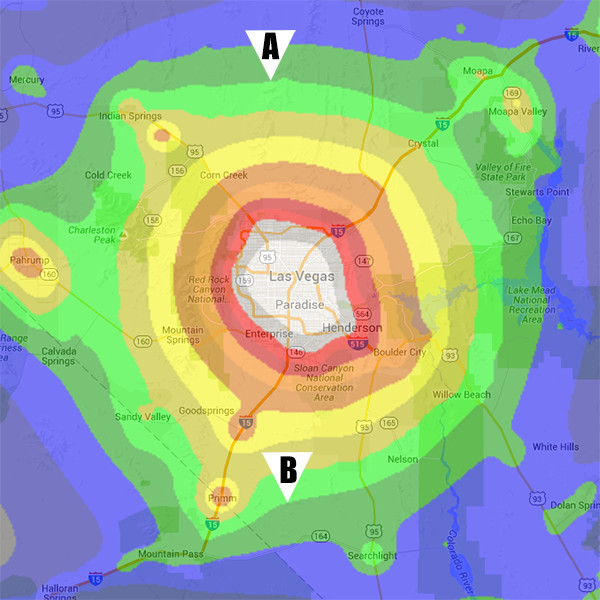
For many people, going somewhere completely devoid of light pollution (a black or gray zone on this map) is not possible without an all-day drive. I know this because I live in Illinois. But a blue or green zone can still provide an impressive view of the milky way. You just have to be more selective in choosing a site, and look at more than just the color zone. The milky way rises in the southeast, crosses the southern horizon, and then sets in the southwest. So you will want to choose a viewing site that does not have any major cities in that direction. Even if the sky overhead is very dark, a light dome from a city can ruin the view if it is located to your south.
This view south was spoiled by the light dome from Springfield, IL
Even though they’re the same color zone, location B is better than location A because you don’t have to look south through the light pollution of Vegas.
Latitude
Above 50° north or so it’s more difficult to see the milky way. It will be much closer to the southern horizon even at it’s highest point. In addition if it’s close to summer solstice the sky will never get completely dark. So you may have to wait until later in the summer to get the best view. On the other hand the farther south you live, the higher up in the sky Sagittarius will rise. Those in the southern hemisphere are privileged to see the milky way high overhead with much more detail than can be seen in the northern hemisphere. If you live in the southern hemisphere, the seasons mentioned above will be opposite, but the months are the same.
Moon Phase
A full moon will drown out all of the faint stars in the sky, including the milky way. Even a slim moon can brighten the sky background quite a bit, so it’s best to avoid it. To see a dark sky all night long, you want to go stargazing during the new moon. A 1st quarter moon will set around midnight. So the hours after that will be dark. A 3rd quarter moon will rise around midnight, and the hours before that will be dark. My favorite tool for quickly finding sunrise, sunset, moonrise, moonset, and twilight times for any location is The Photographer’s Ephemeris. The website is free and they also have a paid smartphone app.