Sodium metabisulfite can be prepared by treating a solution of sodium hydroxide with sulfur dioxide.[3] When conducted in warm water, Na2SO3 initially precipitates as a yellow solid. With more SO2, the solid dissolves to give the disulfite, which crystallises upon cooling.[4]
- SO2 + 2 NaOH → Na2SO3 + H2O
- SO2 + Na2SO3 → Na2S2O5
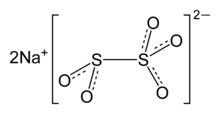
Upon dissolution in water, bisulfite is generated:
- Na2S2O5 + H2O → 2 Na+ + 2 HSO3−

- Sodium bisulfite (or sodium bisulphite, sodium hydrogen sulfite) is a chemical mixture with the approximate chemical formula NaHSO3. Sodium bisulfite is not a real compound,[2] but a mixture of salts that dissolve in water to give solutions composed of sodium and bisulfite ions. It appears in form of white or yellowish-white crystals with an odor of sulfur dioxide. Sodium bisulfite is used in a variety industries such as a food additive with E number E222 in the food industry. It is a reducing agent in the cosmetic and in the bleaching applications.[3][4][5]
- Sodium bisulfite solutions can be prepared by treating a solution of suitable base, such as sodium hydroxide or sodium bicarbonate with sulfur dioxide.
- SO2 + NaOH → NaHSO3
- SO2 + NaHCO3 → NaHSO3 + CO2
- Attempts to crystallize the product yield sodium metabisulfite (also called sodium disulfite), Na2S2O5.[6]
Upon dissolution of the metabisulfite in water, bisulfite is regenerated:
- Na2S2O5 + H2O → 2 Na+ + 2 HSO3−
- Sodium bisulfite is formed during the Wellman-Lord process.[7]